International Celiac Disease Awareness Day 16.05 – gluten-free dishes

On 16.05 we will celebrate the 18th International Celiac Awareness Disease Day. Celiac disease is a disease that more and more people are struggling with. Therefore, on this occasion, we would like to introduce you to the topic of gluten-free diet. In this article, you will also find ideas for gluten-free dishes.
Celiac disease – what you should know about it
A disease known for centuries, but only specified in the 20th century. What exactly is it and how does it manifest itself? That’s what you will learn in this article.
What is celiac disease?
Celiac disease is a disease of the digestive system that results from intolerance of the protein gluten. This disease cannot be infected, it depends on genes. Thus, celiac disease is congenital, it cannot be cured, and it is a lifelong disease. The culprit is the gluten mentioned above. Its harmful effects on a person with the disease lead to changes in the intestinal mucosa and the disappearance of intestinal villi. The villi are essential for the proper absorption and digestion of nutrients supplied by food. In celiac disease, the biggest challenge for the digestive system is the digestion of fats. Their impaired absorption can lead to malnutrition and threaten the body’s normal development.
Symptoms
Different symptoms may be present in each affected person. Among the most common are:
- diarrhea – very often fatty,
- pallor and emaciation – these symptoms are very common in children. It is not uncommon for sick children to have a large, bloated abdomen in addition to the aforementioned symptoms,
- irritability,
- anemia and, consequently, anemia,
- deficiencies of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and minerals such as calcium.
Diagnosis of celiac disease
Celiac disease can only be diagnosed by a gastroenterologist. Once celiac disease is diagnosed, it is best to go to a specialist – a nutritionist, who will prepare individual dietary recommendations and provide ideas for gluten-free dishes.
Parameters that may indicate a celiac disease problem are:
- diarrhea, abdominal pain after eating products containing gluten,
- atrophy of the intestinal mucosa,
- the presence of specific IgA antibodies in the blood – the test for the presence of these antibodies is performed on doctor’s orders,
- the beneficial effect of a gluten-free diet and deterioration of health after eating a diet with gluten.
Gluten – the most important information
Gluten is a mixture of plant proteins found in some cereals. In the case of wheat, it is glutein and gliadin. Gluten, when combined with water, gives a malleable texture, which is desirable, for example, when baking cakes.
Where gluten occurs naturally
Gluten naturally occurs in cereals such as:
- wheat and its varieties, e.g.: spelt, durum, triticale – the gluten proteins are glutein and gliadin,
- Rye – contains the protein secalin,
- barley – the gluten protein in barley is hordenine,
- oats – is naturally gluten-free, but when it grows in the vicinity of other cereals, it can be contaminated with gluten.
Gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet is the only effective form of treatment for celiac disease. Only the elimination of gluten for life prevents the clinical symptoms and improvement of the patient’s health. On such a diet, all products containing gluten and products that may be contaminated with it should be eliminated. A gluten-free diet should be based on gluten-free dishes, based on inherently gluten-free products, such as vegetables, fruits, meat, milk, nuts, and vegetable oils. To ensure an adequate supply of all vitamins and minerals, gluten-free cereals should be introduced into the diet.
Gluten-free cereals
Fortunately, eliminating gluten does not force you to give up all cereals. Many of them are gluten-free and should be eaten by people with celiac disease (and others). They are a valuable source of many B vitamins, as well as magnesium and iron. Such cereals include:
- quinoa – also known as quinoa,
- rice – especially the brown, black, and red varieties,
- amaranth – also known as amaranth,
- buckwheat – you can read more about why it’s worth including in your diet here,
- buckwheat – a source of iron, copper, and manganese, as well as B vitamins,
- corn – corn is often used to make gluten-free bread and pasta,
- gluten-free oats.
The Crossed Grain Trademark
People on a gluten-free diet should direct their attention to products with a crossed grain trademark when shopping. This symbol guarantees that the food has been tested and does not contain gluten. When buying products with this mark, you can be sure that the food is safe for people with celiac disease.

Source: https://www.przekreslonyklos.pl/
What products to watch out for
Gluten cereals and grain products are not the only risks for people with celiac disease. Very often in seemingly gluten-free products, however, it can appear.
Food production and gluten
As a result of food production on the same production lines, many products can be contaminated with gluten. For example, cornflakes, by definition, should not contain gluten. However, if chocolate wheat flakes were previously produced on the same production line, they may be contaminated with it. In this situation, it is best to look for products labeled as gluten-free.
Food additive gluten
Gluten is often added to foods intentionally. It provides the right texture and taste. It is used as an additive in soups, sauces, and dressings. Gluten proteins can also be found in meat and vegetarian products – it affects the shelf life of products.
Gluten – has not one name
Sometimes in products, you will find other names, which specify gluten. Pay attention to whether the ingredients include:
- seitan – often found in vegan meat substitutes,
- hydrolyzed wheat protein, wheat protein, or hydrolyzed vegetable protein,
- hydrolyzed vegetable protein and textured vegetable protein,
- emulsifier, food starch, modified food starch, dextrin, maltodextrin, and vegetable gum.
Some of these additives may come from gluten-free proteins. However, it is worth checking whether a product with the mentioned ingredients has a crossed ear on the package.
Gluten-free diet – is it necessary?
A gluten-elimination diet is necessary for people with celiac disease. It is indicated for people with allergies to gluten, wheat, or other gluten cereals. Exclusion of gluten is also necessary for people with non-celiac gluten hypersensitivity. Note that the diagnosis must be made by a doctor, and the diet should be consulted with a specialist – a nutritionist. A gluten-free diet followed without cooperation with a specialist can be deficient and lead to health problems.

Ideas for gluten-free dishes
Looking for ideas for gluten-free dishes? You can find them in Fitatu®! Each dish has calculated calories and macronutrients. You can also use the Gluten Free Menu, in the Menu selection in Fitatu®. With this feature, the app will suggest you gluten-free recipes tailored to your daily requirements. You can access all recipes and the Menu Selection feature, with Fitatu® Premium.
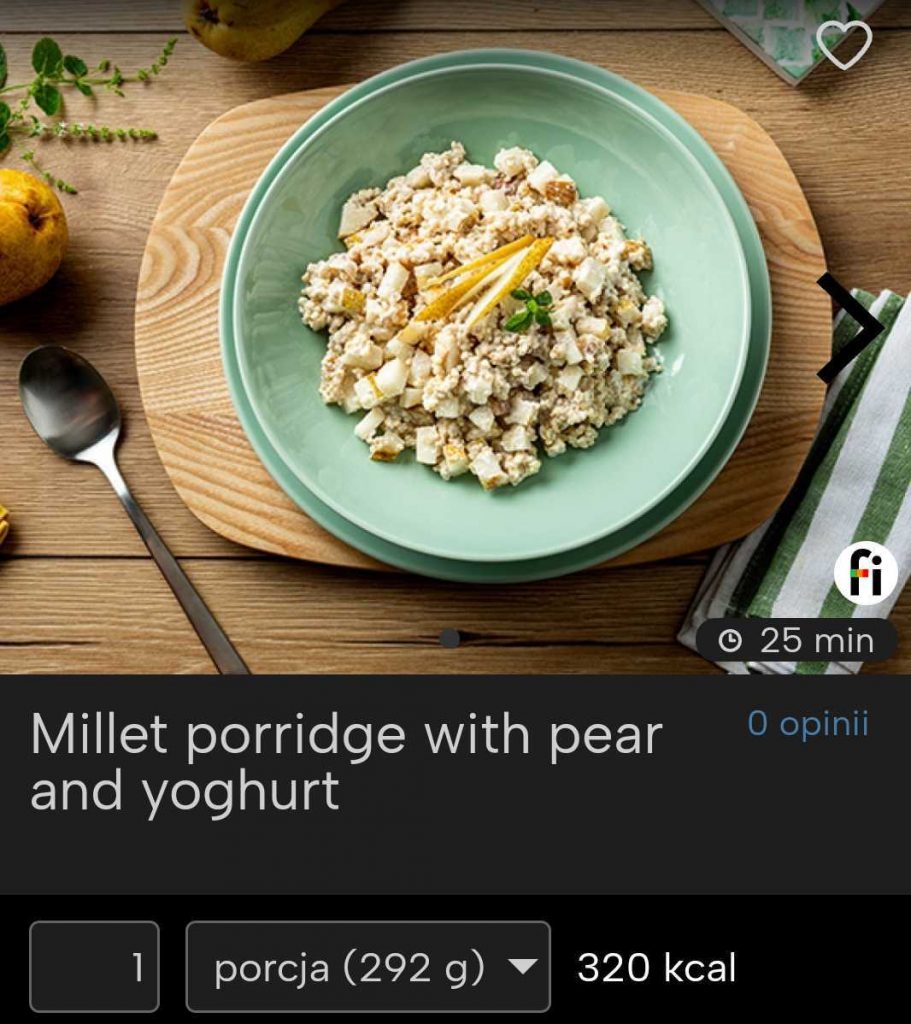
A gluten-free breakfast idea
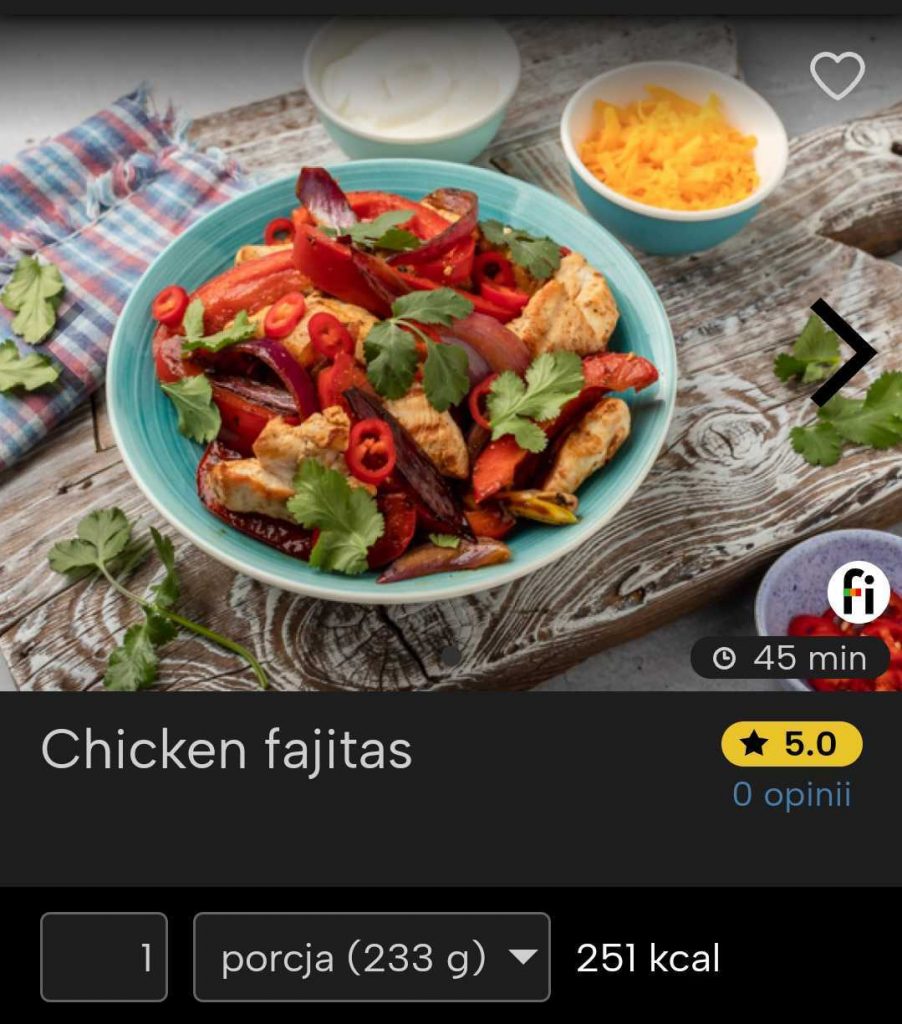
Mexican gluten-free dinner
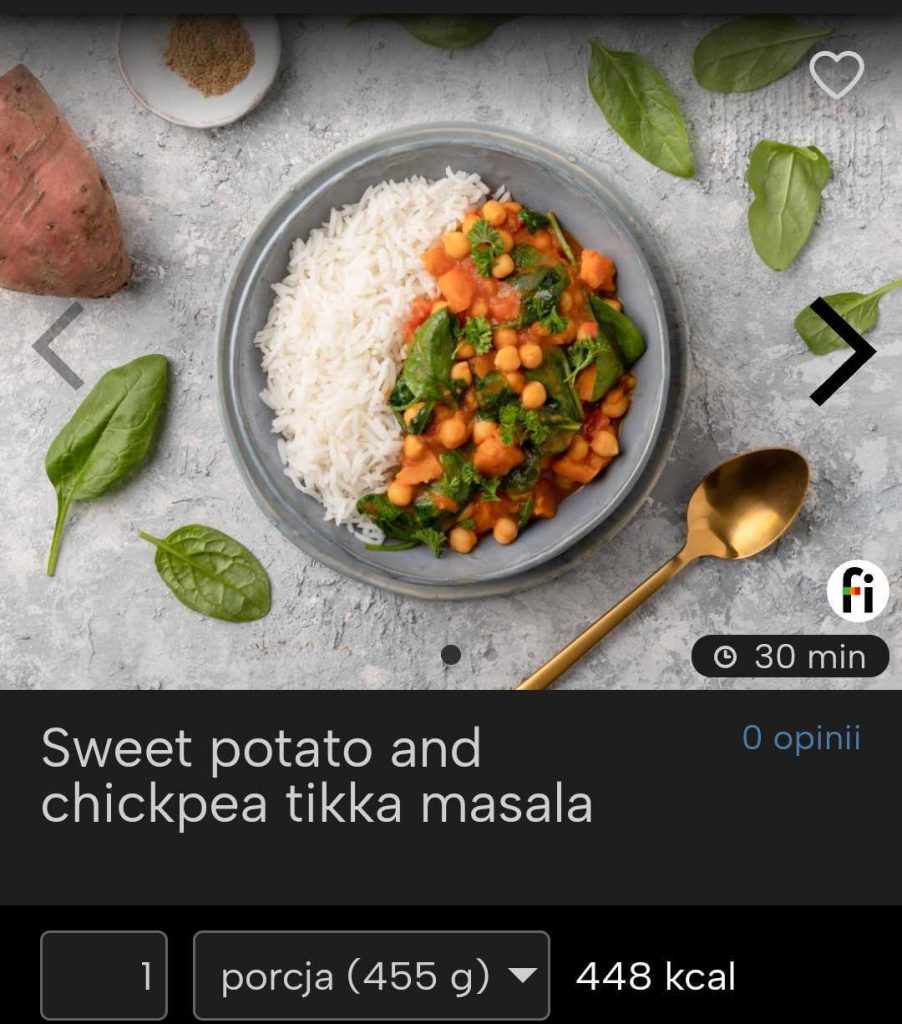
Asia on your gluten-free plate
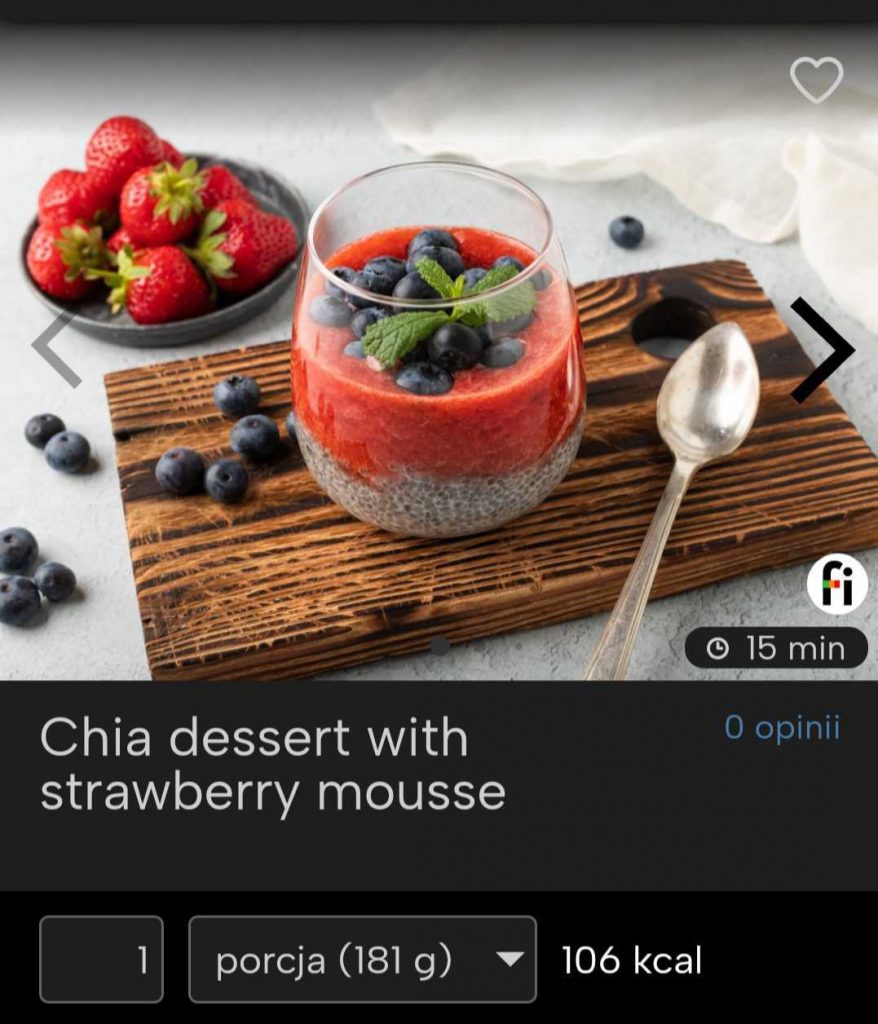
Sweet gluten-free dessert
Fitatu® app
Download the app from the Play Store or Apple Store and find out that a gluten-free diet can be simple! Are you looking for convenience and faster achievement of your nutrition goals? Opt for Fitatu® Premium! We’ve prepared a special discount code for blog readers: CELIAC-D. Go to https://www.fitatu.com/app/order-and-payment and grab a 20% discount on one-year Fitatu® Premium plans.
What else will you find in Fitatu® Premium?
- More than 2,000 recipes plus dozens of new ones every month,
- additional intermittent fasting plans,
- the ability to create shopping lists,
- pre-made menus with meals,
- filtering of products and recipes,
- more synchronization with fit apps,
- web-based access to the app,
- no ads!
Fitatu® support group
Join the Fitatu community on Facebook and achieve your goals together with other users of the Fitatu® app.
Bibliography:
- Dietetyka, żywienie zdrowego i chorego człowieka. Helena Ciborowska, Anna Rudnicka, PZWL, 2018
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/gluten/
- https://www.akademiadietetyki.pl/dietetyka/amarantus-zboze-xxi-wieku/
- https://www.przekreslonyklos.pl/
- https://genelab.pl/opis-produktu/dlaczego-stosujemy-gluten-pszenny-jako-dodatek-do-zywnosci/





