Fat in a weight loss diet — Enemy or ally?

This is a question that sparks many debates in the world of health and nutrition. Is fat really the number one enemy when losing weight, or does it play a key role in maintaining health and well-being? In this article, we delve into the world of fats to dispel any doubts and understand their true role in a weight loss diet. We answer the question of how much fat is worth including in your diet and which types of fats to choose to support health.
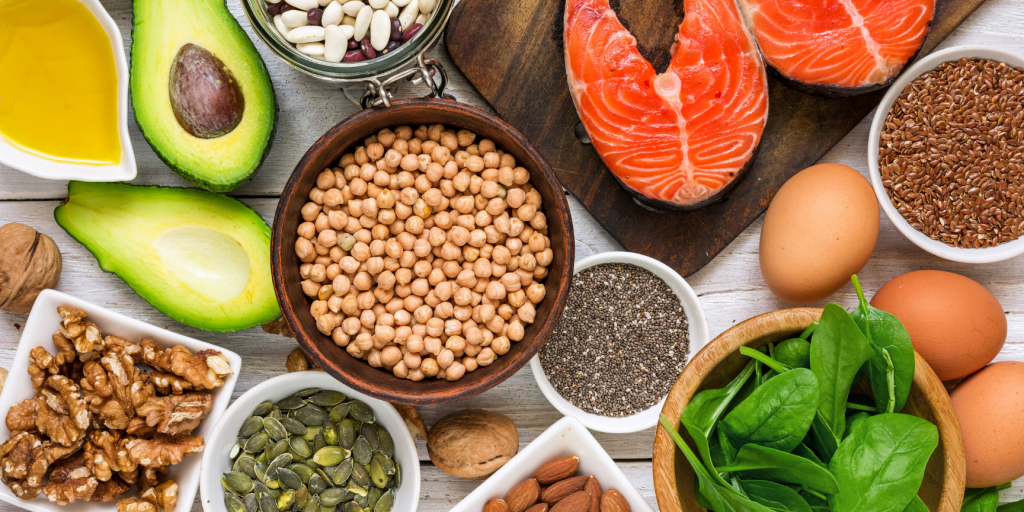
Fat, often demonized, is actually a basic macronutrient that plays an essential role in the functioning of the body. From building cell membranes to acting as a solvent for certain vitamins, to providing energy — fat is more than just a source of calories. Fat influences weight loss, cardiovascular health, and overall well-being.
Fat — the essential macronutrient
The fats, often with a bad reputation, actually build the body, form part of cell membranes, and create fat tissue. Additionally, fat, due to its hydrophobic properties, is a solvent for organic substances that do not dissolve in water, including vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Fat — a source of energy
Fat is also one of the basic macronutrients in the diet. One gram provides 9 kilocalories, which is a relatively high energy content compared to other macronutrients. For this reason, many people opt for a strong reduction of this macronutrient in their diet when losing weight. But is this the right approach? The answer is both yes and no. During weight loss, the most important factor is an energy deficit. A diet that delivers too many calories, even if it’s low-fat, will still prevent weight loss. Indeed, the easiest way to reduce calorie intake is to cut down on fat sources because they provide the most energy. However, such a diet can end up being tasteless, difficult to maintain, and will not lead to sustained weight loss in the long term.
How much fat should you include in your diet?
It is recommended that fat should make up around 25-30% of your daily caloric intake. However, some people feel better on diets with a higher fat content, at the expense of carbohydrates. The most important thing is to provide fat and ensure adequate absorption of vitamins and omega-3 fatty acids. Saturated fatty acids, which do not promote health and lead, among other things, to cardiovascular problems, should be limited to below 10% of the daily intake.
The role of fat in the body
Fat is not only an energy carrier; its structure also helps in the transport and absorption of vitamins in the body. Rich sources of fat contain antioxidants that help fight free radicals and provide essential fatty acids, which support, among other things, the nervous system.
Fat-soluble vitamins
Fats in the diet are important because fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K dissolve in them. Diets that very strictly lower fat levels can lead to problems with properly absorbing these vitamins. As a result, such diets can lead to severe deficiencies and pose a risk to health.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is found in most red vegetables, carrots, leafy greens, and also in butter. It plays many roles in the body, participating in the process of vision, supporting the immune system, and maintaining healthy skin and nails. Vitamin A is also a strong antioxidant, protecting the body from cancer development. To absorb the most vitamin A from food, it is essential to include a fat source in the meal.
Vitamin D
Deficiency of this essential vitamin is common in Poland due to low sun exposure during the autumn and winter months. Vitamin D affects bone health, immune processes, regulates blood pressure, and additionally supports carbohydrate metabolism by improving tissue insulin sensitivity. The main sources of vitamin D are fatty fish, but it is very difficult to meet the recommended daily intake from food alone. Therefore, vitamin D supplementation is worth considering.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E plays a key role in cell membranes — it captures free radicals, thus delaying aging. Adequate amounts in the diet improve the appearance of the skin and support eye health. Vitamin E is a strong antioxidant and is mainly found in vegetable fats such as olive oil, almonds, sunflower oil, nuts, seeds, and grains.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K can be found in leafy vegetables and all green vegetable products. It is chlorophyll that activates enzymes to produce this vitamin in the body. Vitamin K plays crucial roles in the circulatory system — participating in blood clotting processes and supporting bone health by aiding in mineralization.
Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids
Polyunsaturated fatty acids, especially those from the omega-3 and omega-6 families, are essential for health. Since their synthesis does not occur in the body, they must be obtained from food.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids perform many important functions: they reduce triglyceride levels, inhibit blood clot formation, and lower blood pressure, all of which protect the cardiovascular system. Their main sources are fatty fish, unrefined flaxseed oil, and rapeseed oil.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-6 fatty acids lower cholesterol levels and the fraction of LDL lipoproteins, supporting lipid metabolism. To increase omega-6 levels, a diet rich in olive oil and sunflower oil should be followed.
Vegetable oils — a healthier choice
To support weight loss, instead of a significant reduction in fat levels below 25%, focus on fat quality. Replace animal fats like lard, butter, cream, and fatty meats with vegetable oils and fatty fish. Use unrefined oils as additions to salads and dressings. Olive oil and rapeseed oil are great for frying. More about healthy fats can be found in this article.
Limit the intake of these fats on a weight loss diet
Scientific studies show that reducing saturated fatty acids and trans fats in the diet significantly reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases and lowers blood pressure, and also influences weight loss.
Saturated fatty acids
Saturated fatty acids are not health-promoting; they are responsible for clot formation, which is linked to circulatory system problems. A diet high in saturated fats can even lead to coronary disease and heart attack. Avoid them by reducing red meat, especially processed meat, yellow cheeses, and products containing fatty dairy, organ meats.
Trans fats
Due to food processing, fats change their structure. Unsaturated fats, which are liquid, transform into solid fats during technological processes (e.g., margarine, bakery fats). This process creates “trans” bonds. These fats are not health-promoting; they increase LDL levels and decrease HDL levels, negatively impacting lipid metabolism. Moreover, such fat becomes just a source of calories, and unsaturated fatty acids lose their biological properties. It is advisable to eliminate processed foods, which are sources of these fats: pastries, chips, fast food, margarine.
Fun facts about fat
Why do we choose fatty foods? Learn some interesting facts about the special properties of this macronutrient.
Feeling of fullness
Fats are characterized by a high satiety index. This means that eating a fat-rich dish will keep you from feeling hungry quickly. Fat-containing dishes stay in the stomach longer than other macronutrients, prolonging digestion and delaying the feeling of hunger. This can easily limit snacking, which can be particularly problematic during weight loss.
Taste
Fatty dishes are often chosen because they taste better than meals mainly made up of protein or carbohydrates. But why is that? The answer may surprise you, as fat is the carrier of flavor, which is why fatty dishes are more appetizing. For this reason, “light” products often don’t taste as good as their full-fat counterparts.
Fitatu® app
Download the app from the Google Play Store or Apple Store and start tracking your macros with us!
Prefer the web version? No problem. A basic web version is available for our subscribers.
What else is included in Fitatu® Premium?
- over 2000 recipes, plus dozens of new ones every month,
- additional intermittent fasting plans,
- the ability to create shopping lists,
- 7 ready-made meal plans,
- filtering products and recipes,
- more sync options with fitness apps,
- access to the web version of the app,
- no ads!
Fitatu Support Group
Join our Facebook community! Discover inspiring recipes daily, receive support from other healthy eating enthusiasts, and benefit from professional dietitian advice from Fitatu. Get inspired and take care of your health in the best company!