Pickled Foods – Why You Should Eat Them

Pickled foods are low-calorie snacks perfect for summer days. Why should you eat them? What vegetables and fruits can you pickle? How do you choose the right pickled foods in the shop? Get inspired by the recipes from the Fitatu app and fall in love with pickled foods just like we have!
Pickling has been used for centuries to preserve fresh food and prevent it from spoiling quickly. Besides their longevity, pickled foods are also celebrated for their excellent taste. Summer is the season when many people try their hand at making homemade preserves. It’s worth knowing that pickled foods are not only a delicious treat but also a healthy snack.
Why are pickled foods healthy?
High Nutritional Value
During the pickling process, pickled foods do not lose their minerals or vitamins. Therefore, they remain a rich source of these nutrients. What’s more, pickling increases the content of B vitamins. Additionally, during the pickling process, the carbohydrate content in the product decreases. This is due to the lactic acid fermentation process, where bacteria feed on the sugars in vegetables and fruits. In this way, beneficial lactic acid is produced from glucose, significantly reducing the carbohydrate content in the product. Pickling also affects the content and bioavailability of protein. In the case of pickled legume products, lactic acid fermentation increases the content and digestibility of plant proteins. This enhances their nutritional value, making them an excellent source of this macronutrient in the diet.
Pickled Foods as Antioxidants
During the pickling process, polyphenols are formed in vegetables and fruits. These bioactive molecules have a high antioxidant capacity. They act on free radicals, which are responsible for accelerating the ageing process and increasing the risk of many conditions, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
Natural Probiotics
Pickled foods have a significant impact on gut flora. Pickled vegetables and fruits can be called natural probiotics. By providing lactic acid, they support gut health. Lactic acid is not broken down during digestion in the upper digestive tract, allowing it to colonize the large intestine. In this way, it creates a microbiome that protects the intestines from unwanted pathogens, thereby modulating the immune system. Eating pickled foods supports the body’s immune processes. However, it’s essential to remember that lactic acid remains in pickled foods that have not been heated or pasteurized. Lactic acid breaks down at high temperatures, so cooked sauerkraut will not provide as many benefits as its uncooked version.
Pickled Foods as Prebiotics
Pickled foods are prebiotics because they provide food for the healthy bacteria inhabiting the large intestine—exopolysaccharides (EPS). These substances are produced by the action of lactic acid formed during the pickling of vegetables and fruits. These substances nourish the bacteria that inhabit the large intestine. They also have a positive effect on lipid metabolism by trapping cholesterol deposits, consequently lowering the total cholesterol level in the body.
Which Pickled Foods to Choose?
The best choice is pickled foods from a reliable source. Those prepared in barrels may contain more pathogenic microorganisms than pickled foods purchased in a sealed bag. When vegetables have free access to oxygen, and leakage allows foreign bacteria to penetrate, uncontrolled fermentation can occur. Consequently, it is unknown what substances are in the brine and vegetables themselves. Consuming such products can negatively affect the digestive system, especially for individuals with gastrointestinal issues.
What Can You Pickle?
Nowadays, many pickled specialties are available on store shelves. From traditional Polish sauerkraut or pickled cucumbers to Korean kimchi or pickled lemons. You can pickle various vegetables such as cauliflower, radish, pepper, green beans, or carrots. Only your imagination can limit you in pickled experiments. However, it is not recommended to pickle dark green leafy vegetables as they may spoil before pickling. The most crucial rule in pickling is to choose fresh produce. Vegetables and fruits that are starting to spoil are not suitable for pickling. Popular pickled fruits include lemons, apples, pears, or peaches.
Recipes with Pickled Foods in the Fitatu App
In the Fitatu app, you will find hundreds of inspirations, including dishes with pickled foods. Try the following recipes and share your opinion with us under the recipes in the app.
Wrap – Quick Lunch
Wraps are a tasty, simple, and quick option. You can also enjoy pickled foods in this form. Pickled cucumbers or sauerkraut will be an excellent addition, enhancing the taste of the dish and providing essential vitamins.
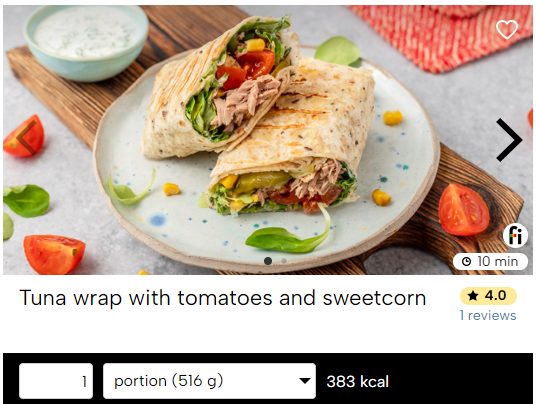
Tuna wrap with tomatoes and sweetcorn
Sauerkraut with Potatoes
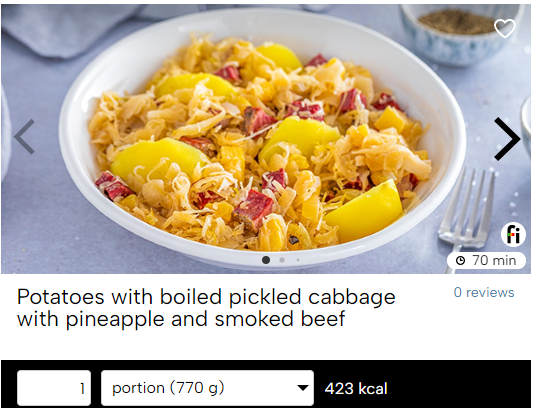
The combination of potatoes and sauerkraut is simply splendid. This meal provides a significant source of fibre and vitamin C. You can add your favourite meat, fish, tofu, or legumes as a side. We present a recipe for an unusual twist with the addition of pineapple and beef.
Potatoes with boiled pickled cabbage with pineapple and smoked beef
Light Summer Salad
On hot days, a light salad is always a good choice. Use seasonal vegetables like asparagus and add some pickled vegetables. Try our recipe for a salad with asparagus and pickled cauliflower.
Asparagus and Parma ham salad with roasted garlic and pickled cauliflower

Hot Dog with Pickles
Hot dogs are a beloved dish by many. Prepare a healthier version of a hot dog with our recipe.
Hot dog wiht sausage, chinese cabbage and pickled cucambers

Spread – A Delicious Addition to Bread
Spreads make a great addition to bread. Popular spreads like butter or margarine consist mainly of fat. Vegetable-based spreads also provide protein, dietary fibre, vitamins, and minerals.
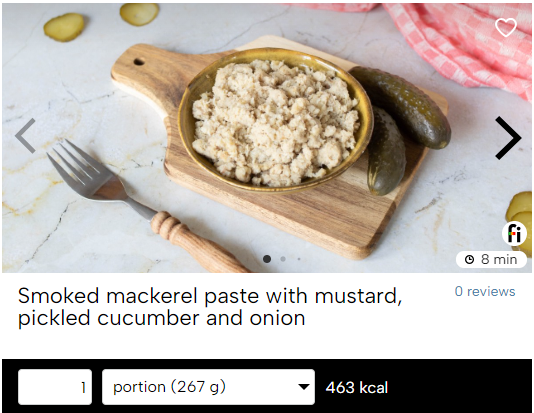
Smoked mackrel paste with mustard, pickled cucumber and onion
Fitatu® Support Group
Reaching your goal is easier with the support of others! Join our Fitatu Facebook group and achieve your goals together with other Fitatu® app users. With the group members, you can share your results every day and motivate each other to keep going.

Fitatu® App
Not yet familiar with Fitatu®? Download the app from the Play Store or Apple Store and start taking charge of your health with us! Do you want to have access to all the features? Go for Fitatu® Premium! For blog readers, we have a special discount code: PICKLING. Go to https://www.fitatu.com/app/order-and-payment and claim a 20% discount on Fitatu® Premium annual plans. The code combines with other promotions.
Bibliografia:
- Şanlier, N., Gökcen, B. B., & Sezgin, A. C. (2017). Health benefits of fermented foods. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 59(3), 506–527. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1383355
- https://dietetycy.org.pl/kiszonki/
- https://pl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Egzopolisacharydy
- Axelle Septembre-Malaterre, Fabienne Remize, Patrick Poucheret , Fruits and vegetables, as a source of nutritional compounds and phytochemicals: Changes in bioactive compounds during lactic fermentation, Food Research International (2017), doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.09.031
- https://pacjent.gov.pl/diety/jedz-kiszonki-wzmocnic-odpornosc-przed-zima
- Overview of materials intended for contact with food. What should kitchenware be made of?
- Demystifying fat: How many calories are in a fat?
- Sweet but smart snacks for kids : A look at popular sweets and healthier alternatives
- Fat in a weight loss diet — Enemy or ally?
- 11 tips on how to prepare meals faster